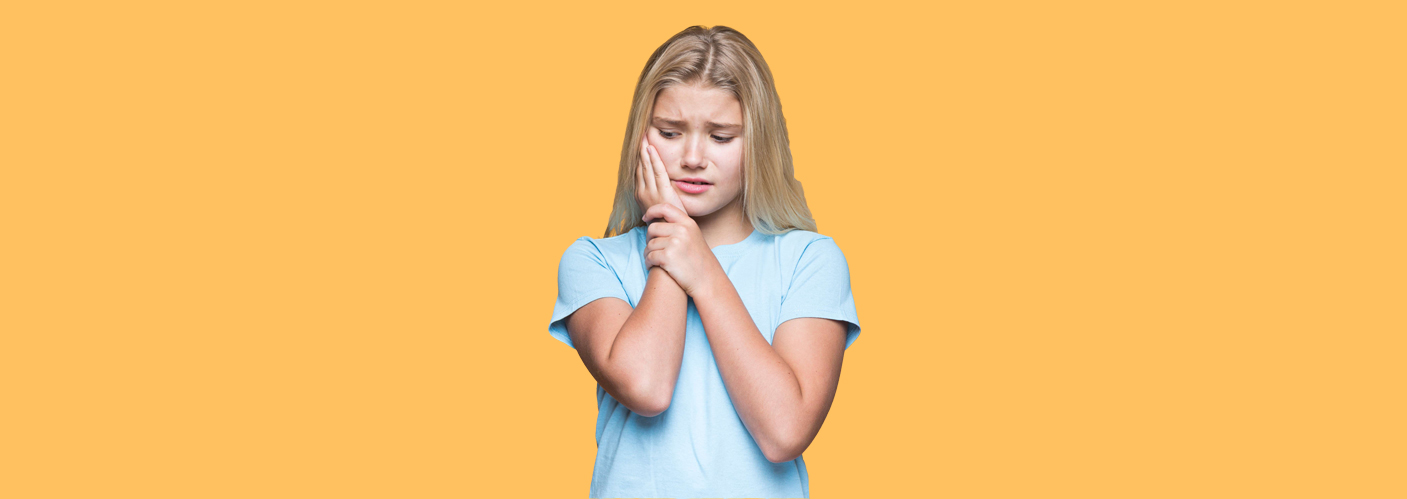
Tooth pain: Tooth pain is considered one of the most unpleasant experiences for most people. So let’s talk about it and try to ensure your child never goes through this experience.
Here is a list of some of the most common causes of tooth pain
- Tooth decay
- Tooth fracture
- Damaged tooth filing (recurrent caries)
- Irritated or inflamed pulp (tooth nerve)
- Excessive repetitive motions: chewing gums or grinding teeth (mostly in the case of kids).
How Does tooth pain present?
- Sharp but transient sensation when eating sweats, cold or hot food or drinks. Sensation stops immediately aggravating factor is removed
- Sharp sensation that lingers after aggravating factor (listed above) is discontinued
- Pain that starts on its own without any aggravating factor, wakes patient up at night, relieved by OTC pain medication
- Pain that starts on its own without any aggravating factor, wakes patient up at night, not relieved by OTC pain medication
When you should visit your dentist:
- At the first sign of tooth pain or sensitivity
Diagnosis of tooth pain:
Physical exam: your dentist will assess your condition by asking some questions about the pain, he will then inspect the area of concern.
X-rays: sometimes, in order to ascertain the cause of pain, your dentist, might need a radiograph. The radiograph will show the extent of the cavity (if the pain is caused by caries) as well as if there is any evidence of infection spread. The radiograph can also detect cracks if present.
Treatment available for tooth pain:
Based on your child’s presenting complaints, clinical observation, and results of other diagnostic tools explored, Dr. Alex Okoye (Dr. O) will be able to determine what treatment is most suitable for your child. Treatments could range from conservative fillings, crowns to pulpotomies/pulpectomies (baby root canals) or sometimes extraction.
Filings: If the decay is confined within the enamel or dentine, a filling or crown could be recommended. Here the decayed part of the tooth is removed and replaced by inert material.
Root canal: preferred by many dentists if it’s determined that the bacterial infection has spread to the nerve but is still confined in the tooth apparatus.
Extraction: Preferred by many dentists if it’s determined the bacterial infection has spread out of the tooth apparatus and into the bone. There are also other factors that might inform your dentist’s decision.
Antibiotic is given to the patient if there is fever or swelling of the jaw.
What can you do to prevent tooth pain:
Diet: avoid sugar-containing food or drinks particularly non-milk sugars products. Avoid carbonated drinks, fruit juices can also cause tooth erosion. The best advice is to consume water and drink milk for children.
Fluoride: water fluoridation is very effective and safe to prevent caries. Kids older than six months can be given daily fluoride supplements in the form of drops or tablets, fluoride toothpaste led to the decline of caries in many kids.
Fluoride sealants: Coating placed by your dentist in pits and fissures of permanent teeth that can help to prevent the growth of caries.
Oral hygiene:
- Proper brushing with fluoridated toothpaste twice daily
- Electric brushes can be useful for ones with poor dexterity.